Architecture
There is many architecture to install a K8S cluster. according to the aim or costs, you can chose the adequat design.
K8S architecture bellow:
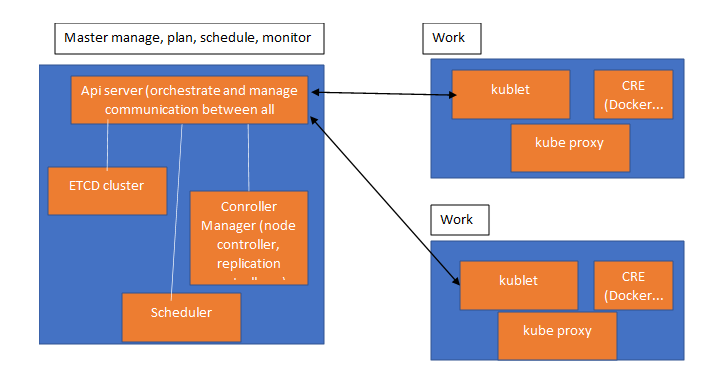
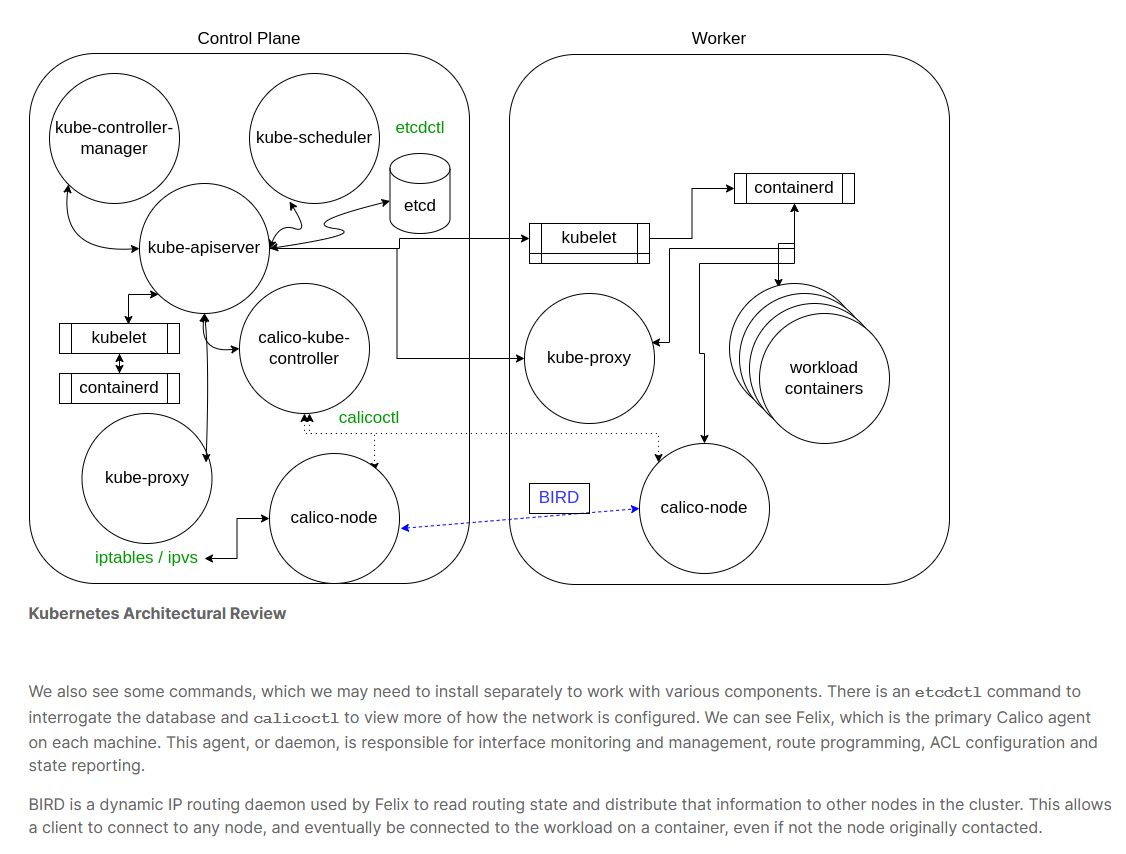
most interfaces used in kub: CRI as Container Runtime Interface, CNI as Containes Network Interface, CSI as Container Storage Interface

ETCD Database
Etcd database store all information about cluster: Nodes, Pods, Config, secret, Accounts, Roles, Binding,…
- Direct installation bellow :
wget -q --https-only \ "https://github.com/coreos/etcd/releases/download/v3.3.9/etcd-v3.3.9-linux-amd64.tar.gz"
- Run etcd service via la commande
./etcd
- change the value into database with etcd control:
./etcdctl set key value
- check installed version of etcdctrl :
./etcdctl --version
Be attention, you should alwayse check etcdctrl version because there a difference between commands of V2 and V3
- Change control etcd version:
export ETCDCTL_API=3
./etcctrl version
./etcdctrl
- Changer une valeur et la récupérer avec la version 3 du control etcd
./etcdctrl put key1 value1 ./etcdctrl get key1
- The endpoint to communicate with database is 'advertise-client-urls' into etcd.service
- If installation is with kubeadm :
Kubectl get pods –n kube-system Kubectk exec etcd-master –n kube-system etcdctl get / --prefix –key-only
- In HA, ip adresses are in etcd.service (initial_cluster_etcd)
- Default ETCDCTRL is Version 2.
- ETCDCTRL can communicate with ETCD API SERVER with certificat :
kubectl exec etcd-master -n kube-system -- sh -c "ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get / --prefix --keys-only --limit=10 --cacert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --cert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt --key /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key"
API Server
- Installtion from scratch as a service in your node :
https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.13.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-apiserver
- API server execute opertaions bellow :
- Authenticate user
- Validate Request
- Retrieve data
- Update ETCD
- Scheduler
- Kublete
Example of API’s requests : curl –X POST /api/v1/namespaces/default/pods
- In kube-apiserver.service, the importante conf are : etcd-cafile, etcd-certfile,etcd-keyfile, kubelet-cacertficate, kubelet-client-certificate, kubelete-client-key and kubelete-https
- With kubeadm, configurations are in : /etc/kuberntes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
- To check options : /etc/systemd/systemd/system/kube-apisever.service
- We can also see the running process :
ps –aux|grep kube-apiserver
Kub Controller Manager
- Controllers : watch status and remediate sitauation, node monitor period = 5s, Node monitor grace period = 40s, POD eviction timeout = 5m
- Example : node controller call api manager to have informations about nodes
- There is many controller and all are in one process controller
Conf is in the file /etc/systemd/system/kube-controller-manager.service
The process is : ps –aux|grep kube-acontroller-manager
- Installation :
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.13.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-apiserver
- Configurations are in kube-controller-manager.service
- If installation is wit kubeadm: conf is into the pod : cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml
Kub Scheduler
- Role of scheduler is : Which pod goes in wich node.
- Scheduler filter nodes to know if cpu and memory is suffisent to put the pod and rank thems
- Installation :
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.13.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-scheduler
- If scheduler is installed with kubeadm, the conf : cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler.yaml
Process : ps –aux|grep kube-scheduler
Kubelet
- Kubelet recieve info from the apiserver in wich get infi from the scheduler to create pod
- So the kubelet register node, create pods, monitor node and pods,
- Installation:
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.13.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubelet
- To check process kubelet : ps –aux|grep kubelet
Kube Proxy
- The role of kube proxy (process kube proxy) is looking for services that are created and create a iptable into the node to reroute packet from the ip service to the pod ip.
- Pi : un service est virtuel et n’a pas d’interface comme les pods ni the processus actif, il est juste dans la mémoire de kub, mais comment les autres nœuds peuvent y accéder
- Installation:
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.13.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-proxy
- The conf is into kube-proxy.service
- If installation is with kubeadm, the object created is a deamonset with two pods
Pods
- Create a singl pod into K8S cluster :
Kubectl run nginx –image nginx
- Commands pods:
Kubectl get pods
- Pods with yaml :
kubectl run nginx-test --image nginx --dry-run=client -o=yaml > pod.yaml
- To apply a yaml file
Kubectl apply –f pod.yaml
Replicat Set
- The difference between replicaset and replicacontroller is selector
- The main aim of replicatset is to maintain the number of pods
Deployment
- Deployments regroup replicatset and pods difinitions,
- Command to create file fo deployment object :
kubectl create deployment --image=nginx nginx --replicas=4 --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-deployment.yaml
- Command to scale a deployment
kubectl scale deployment nginx --replicas=4
Services
- Services types :
- NodePort
- ClusterIP
- LoadBalancer
- To have yaml file
Kubectl create service clusterip redis –tcp=6379:6379 –dryrun=client –o yaml (change selectors) Or kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --target-port=8000 –dry-run=client –o yaml Or to expose a pod with own selectors kubectl expose pod redis --port=6379 --name redis-service --dry-run=client -o yaml
- Create a Service named nginx of type NodePort to expose pod nginx's port 80 on port 30080 on the nodes:
kubectl expose pod nginx --type=NodePort --port=80 --name=nginx-service --dry-run=client -o yaml
Namespaces
- Namespace is used to isolate environement like dev and prod
- Commad to get all pods in all namspaces :
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces or -A
- Command to change namespace :
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=digicactus-ns
- Command to configure or change resource quota
cat < compute-resources.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ResourceQuota metadata: name: compute-resources namespace: dev spec: hard: requests.cpu: "1" requests.memory: 1Gi limits.cpu: "2" limits.memory: 2Gi EOF
- Command to know hwo many pods are into namespace
kubectl get pods –namespace=nom_du_namespace